Ecoregion Antwerp, Belgium
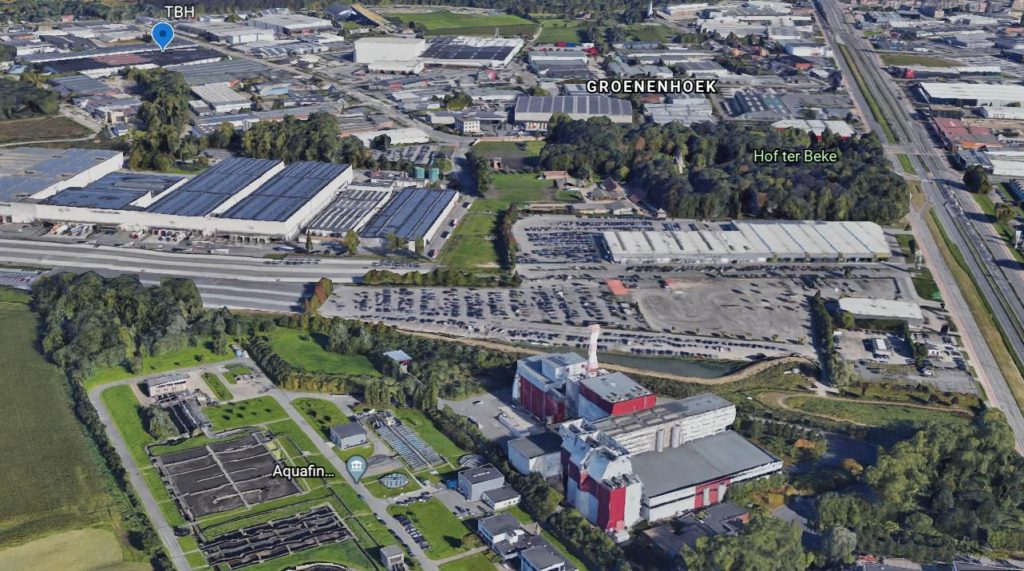
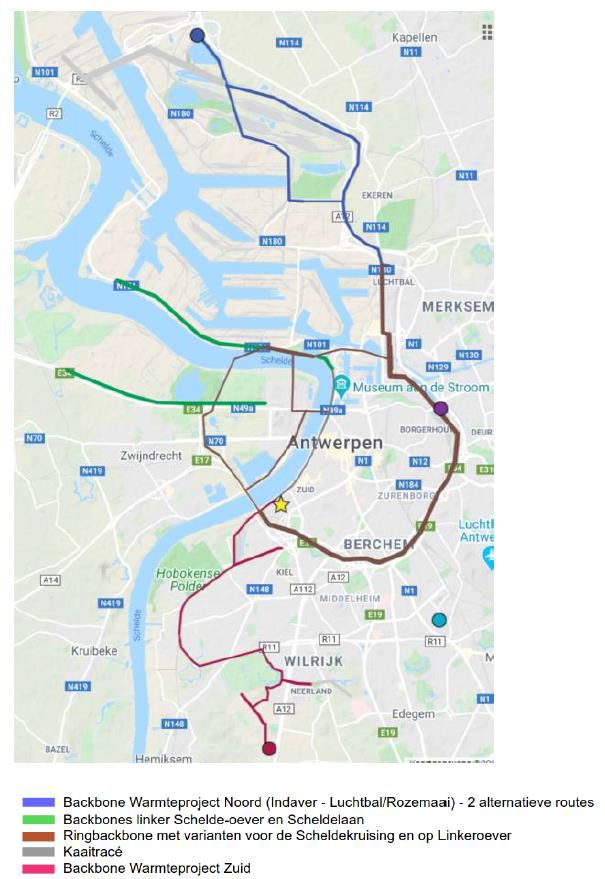
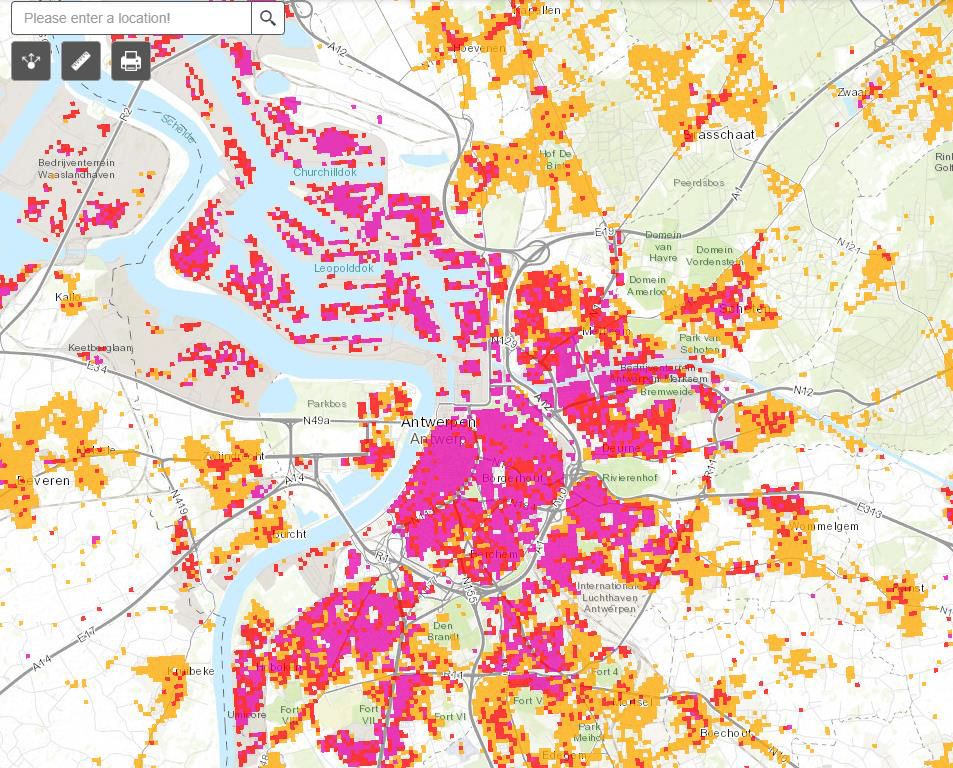
The industrial region Antwerp, with over 500.000 people living in the city centre and surrounding districts, is located next to the river Scheldt. Antwerp can count on the second largest port of Europe and on two interesting business parks near the port area. Within the project framework and in order to build up the Antwerp eco-region, 2 industrial areas are identified: Terbekehof (TBH) and Kanaalkant (KK).The city has a total heat demand of 31 PJ, of which 14,5 PJ is in areas with a heat demand density of more than 300 TJ/km². Excess heat facilities (including waste-to-energyfacilities) with a theoretical output of more than 50 PJ are located within less than 15 kilometres away from the city centre. According to the Pan-European Thermal Atlas 4.3 Antwerp is identified as a heat synergy region (NUTS3 region ID: BE211) with a very high priority level 1.
Localisation
Terbekehof (TBH)
The objectives
Aim
To maximize the energetic efficiency by recovering further waste heat for DHN
Ambition
To expand the heat network beyond the city of Antwerp and surroundings.
In the meantime, the dimensioning of the first phase of the heat network considers the future capacity of the second phase. Together with POM Antwerp and the trade association (HIW), the city of Antwerp is working hard to realize the most sustainable, eco-friendly and energy-efficient business park in Flanders in terms of infrastructure, energy, green and waste policy.
Yes, we believe in energy cooperation
Localisation
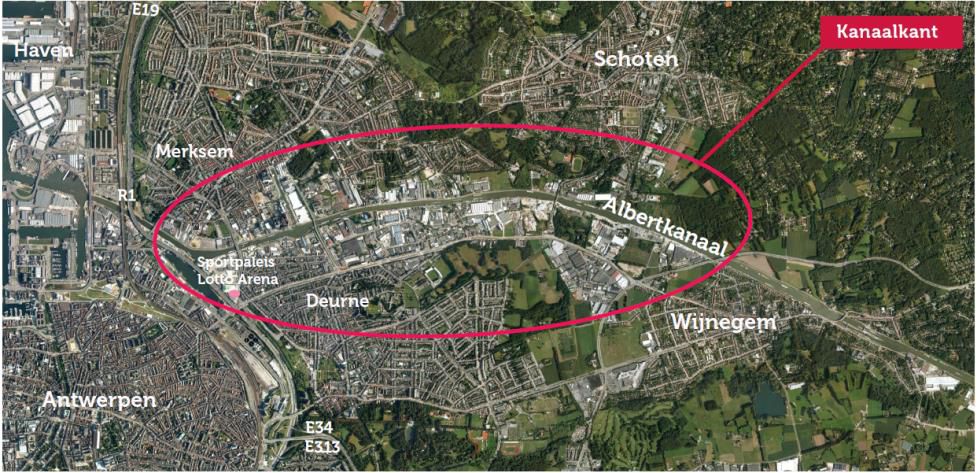
Kanaalkant (KK)
The objectives
Aim
To detect projects that will leverage the industrial area in the direction of the circular ambitions of Kanaalkant, especially realising a far-reaching sustainable, circular industrial zone in the coming future. Exchange-projects for heat and cold can function as a leverage.
Ambition
The authorities no longer work from their ownpoint of view but combine their means through an area-based approach.
Moreover, a circular sustainability study has been carried out with a focus on feasible project plans at Kanaalkant, including a heat-exchange plan between users of a so-called food-cluster and residential area. From the inventory and consultation with stakeholders it was concluded that there was no possibility of mutual interaction exchange of residual heat between companies. Nonetheless, the realisation of a heat network with the nearby residential area is realistic. Other cases can be investigated with the R-ACES tools.